Introduction
When I first heard the term MLOps, I thought it was just “DevOps but for ML.”
Simple enough, right? Deploy some models, automate a few scripts, done.
But the deeper I went, the more I realised:
Machine Learning moves differently. Models drift. Data changes. Accuracy drops. Pipelines break. And unlike a normal application, ML systems need constant monitoring and retraining.
That’s where MLOps comes in.
It brings order to the chaos of machine learning workflows.
Let’s walk through MLOps in a beginner-friendly, practical way.
My Earlier Understanding of MLOps
I assumed MLOps was mostly about:
- Deploying ML models
- Training automation
- Using tools like MLflow or Kubeflow
Pretty straightforward.
But every real-world ML project quickly breaks that illusion:
- Datasets keep changing
- Model accuracy slowly decreases
- Experiments multiply fast
- Keeping track of versions becomes messy
- Improving one part breaks another
Basically: ML models don’t stay stable. They age like fruit, not like software.
And that’s exactly why MLOps exists.
My New Understanding of MLOps
Now I understand that MLOps = DevOps + Machine Learning Lifecycle.
It is a set of practices that help you:
- Build
- Train
- Deploy
- Monitor
- Re-train
- Scale
machine learning models reliably.
Why do we need MLOps?
Because ML systems are alive.
The data changes → the model changes → performance changes → business impact changes.
MLOps ensures:
- Models stay accurate in production
- Retraining happens automatically
- Data pipelines remain stable
- Experiments are traceable
- Deployments are repeatable
- Teams collaborate smoothly
Without MLOps, ML systems collapse fast.
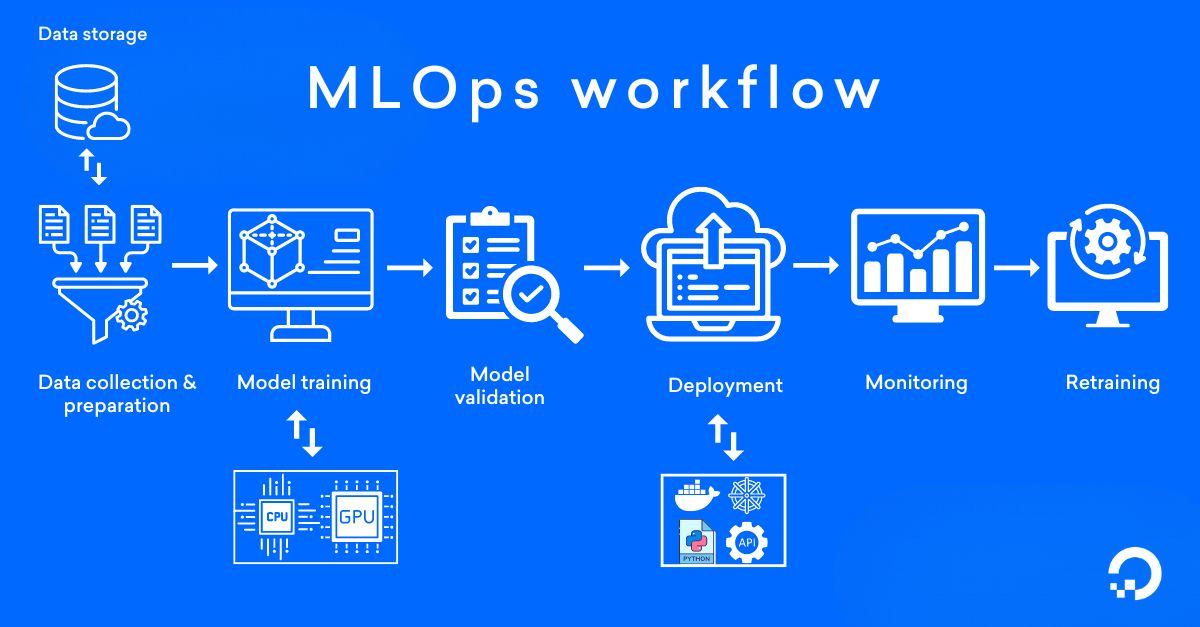
Core Stages of the MLOps Lifecycle
Here’s the flow most MLOps setups follow:
1. Data Collection
Collecting raw data from APIs, streams, databases, or logs.
2. Data Versioning
Using tools like DVC, Delta Lake, or LakeFS to track dataset versions.
3. Data Preprocessing
Cleaning, labeling, transforming, and featurizing data.
4. Experimentation
Running multiple model experiments using:
- MLflow
- Weights & Biases
- TensorBoard
Everything (metrics, parameters, accuracy) gets tracked.
5. Model Training
Training models at scale using GPUs or distributed clusters.
6. Model Packaging
Converting models into deployable formats:
- SavedModel
- ONNX
- Pickle
- TorchScript
7. Model Deployment
Deploying models on:
- REST APIs
- Batch pipelines
- Edge devices
- Kubernetes
Tools: BentoML, FastAPI, TorchServe, Vertex AI.
8. Monitoring
Tracking:
- Model accuracy
- Latency
- Data drift
- Prediction drift
- Concept drift
9. Continuous Retraining
Automated pipelines retrain models when performance drops.
This cycle keeps repeating.
Key Concepts You Must Know
Model Versioning
Because models evolve with new data.
Feature Stores
Centralized place to store and reuse features across models.
Examples: Feast, Hopsworks.
Data Drift & Concept Drift
Drift is the biggest reason models fail in production.
Model Registry
A catalog of models, versions, and metadata.
Orchestration Pipelines
Automated workflows using:
- Kubeflow Pipelines
- Airflow
- Flyte
- Metaflow
CI/CD for ML (CI/CD/CT)
Besides code, ML systems need:
- Continuous Training (CT)
- Continuous Monitoring (CM)
Example MLOps Stack
A modern MLOps workflow might include:
- GitHub / GitLab – Code versioning
- DVC / LakeFS – Data versioning
- MLflow / W&B – Experiment tracking
- FastAPI / BentoML – Model serving
- Kubernetes – Scaling models
- Prometheus + Grafana – Monitoring
- Airflow / Kubeflow – Pipelines
- S3 / MinIO – Artifact storage
Together, they create a complete ML ecosystem.
Real-World Use Cases
MLOps is behind most AI-powered systems you interact with daily:
- Netflix recommendation engine
- Fraud detection models
- Autonomous vehicles
- Chatbots & NLP systems
- E-commerce ranking algorithms
- Healthcare prediction models
Without MLOps, these systems would break quickly.
Resources That Helped Me
-
Google MLOps Guide
Best conceptual explanation of ML production systems. -
Made With ML
Easy tutorials for beginners. -
MLflow Documentation
Perfect for learning tracking, registry, and deployment. -
YouTube: Goku Mohandas
Clear breakdowns of modern MLOps patterns.
Conclusion
MLOps is no longer optional—it’s essential.
As AI grows, so does the need for stable, reliable machine learning pipelines.
Understanding MLOps helps you:
- Build scalable ML systems
- Automate complex workflows
- Track experiments cleanly
- Deploy models confidently
- Monitor them reliably
This blog is just the beginning.
Soon, I’ll dive deeper into:
- Model versioning explained
- Building pipelines with Kubeflow
- Deploying ML models using FastAPI
- Understanding data drift & retraining
- End-to-end MLOps project for beginners
MLOps isn’t just a workflow—it’s the backbone of real-world AI.